Komposisyon
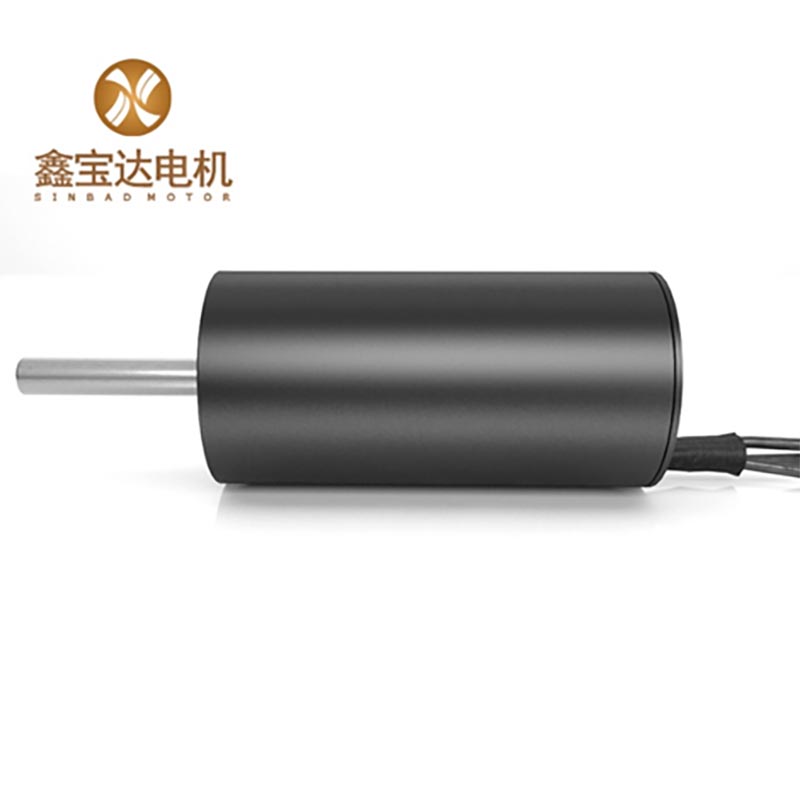
1. Permanenteng magnet DC motor:
Kini naglangkob sa stator pole, rotors, brushes, casings, ug uban pa.
Ang mga poste sa stator ginama sa permanenteng magnet (permanent magnet steel), ginama sa ferrite, alnico, neodymium iron boron ug uban pang materyales. Sumala sa estruktura nga porma niini, kini mahimong bahinon sa daghang mga tipo sama sa cylindrical type ug tile type.
Ang rotor kasagarang ginama sa laminated silicon steel sheets, ug ang enameled wire gisamad sa tunga sa duha ka slots sa rotor core (adunay tulo ka windings sa tulo ka slots), ug ang mga joints kay welded sa metal sheets sa commutator.
Ang brush usa ka conductive nga bahin nga nagkonektar sa power supply ug ang rotor winding, ug adunay duha ka kabtangan sa conductivity ug wear resistance. Ang mga brush sa permanenteng magnet nga mga motor naggamit sa single-sex metal sheets o metal graphite brush, ug electrochemical graphite brush.
2. Brushless DC motor:
Gilangkuban kini sa permanenteng magnet rotor, multi-pole winding stator, position sensor ug uban pa. Ang brushless DC motor gihulagway nga walay brush, ug naggamit sa mga semiconductor switching device (sama sa mga elemento sa Hall) aron makaamgo sa electronic commutation, nga mao, ang mga electronic switching device gigamit sa pag-ilis sa tradisyonal nga contact commutators ug brushes. Kini adunay mga bentaha sa taas nga kasaligan, walay commutation spark, ug ubos nga mekanikal nga kasaba.
Ang sensor sa posisyon nag-commutates sa kasamtangan sa stator winding sa usa ka piho nga han-ay sumala sa pagbag-o sa posisyon sa rotor (nga mao, nakamatikod sa posisyon sa rotor magnetic pole nga may kalabutan sa stator winding, ug nagmugna og usa ka position sensing signal sa determinado nga posisyon, nga giproseso sa signal conversion circuit ug dayon gikuha. Kontrola ang power switch circuit, ug ibalhin ang winding nga relasyon sumala sa usa ka piho nga logic nga relasyon).

2. Brushless DC motor:
Gilangkuban kini sa permanenteng magnet rotor, multi-pole winding stator, position sensor ug uban pa. Ang brushless DC motor gihulagway nga walay brush, ug naggamit sa mga semiconductor switching device (sama sa mga elemento sa Hall) aron makaamgo sa electronic commutation, nga mao, ang mga electronic switching device gigamit sa pag-ilis sa tradisyonal nga contact commutators ug brushes. Kini adunay mga bentaha sa taas nga kasaligan, walay commutation spark, ug ubos nga mekanikal nga kasaba.
Ang sensor sa posisyon nag-commutates sa kasamtangan sa stator winding sa usa ka piho nga han-ay sumala sa pagbag-o sa posisyon sa rotor (nga mao, nakamatikod sa posisyon sa rotor magnetic pole nga may kalabutan sa stator winding, ug nagmugna og usa ka position sensing signal sa determinado nga posisyon, nga giproseso sa signal conversion circuit ug dayon gikuha. Kontrola ang power switch circuit, ug ibalhin ang winding nga relasyon sumala sa usa ka piho nga logic nga relasyon).
3. Taas nga tulin nga permanenteng magnet nga walay brush nga motor:
Kini gilangkuban sa stator core, magnetic steel rotor, sun gear, deceleration clutch, hub shell ug uban pa. Ang sensor sa Hall mahimong i-mount sa tabon sa motor alang sa pagsukod sa katulin.
Pagkumpara sa mga brushed motors ug brushless motors
Ang kalainan sa prinsipyo sa electrification tali sa usa ka brushed motor ug usa ka brushless motor: Ang usa ka brushed motor mao ang mekanikal nga commutated pinaagi sa usa ka carbon brush ug usa ka commutator. Ang usa ka brushless motor kay elektroniko nga gi-commutate sa usa ka controller base sa induction signal
Ang prinsipyo sa suplay sa kuryente sa brushed motor ug brushless motor lahi, ug lahi usab ang internal nga istruktura niini. Alang sa hub motors, ang output mode sa motor torque (kon kini gi-decelerate sa mekanismo sa pagkunhod sa gear) lahi, ug ang mekanikal nga istruktura niini lahi usab.
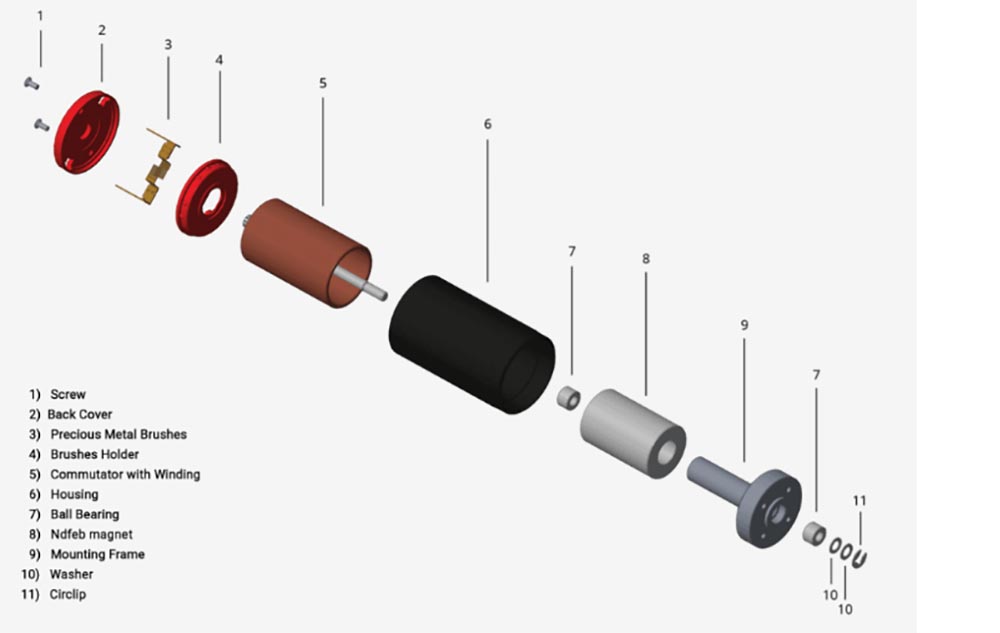
walay core nga brushed dc motor
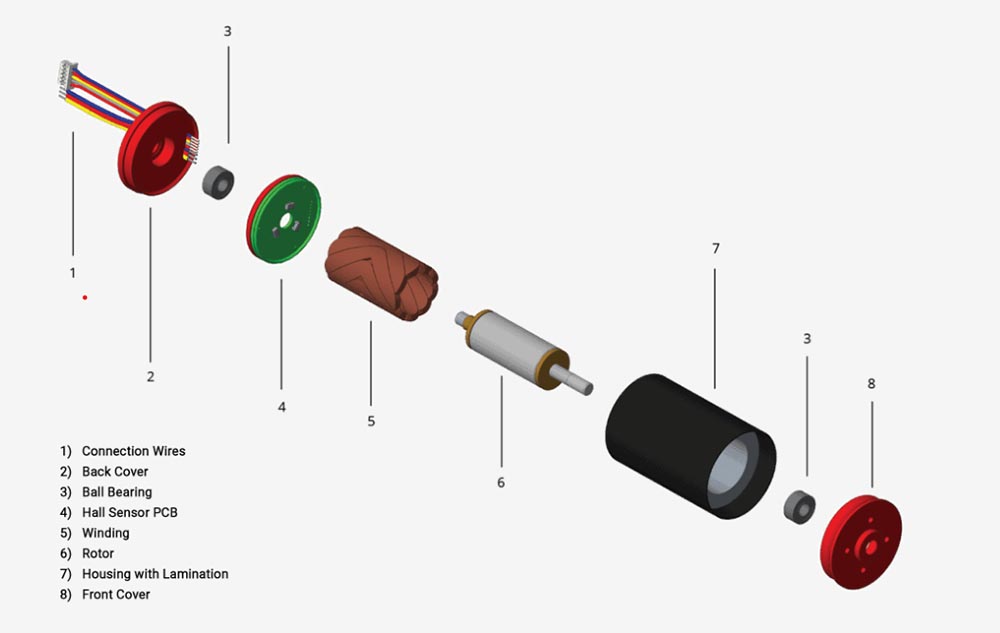
walay core nga brushless dc motor
Oras sa pag-post: Hunyo-03-2019

